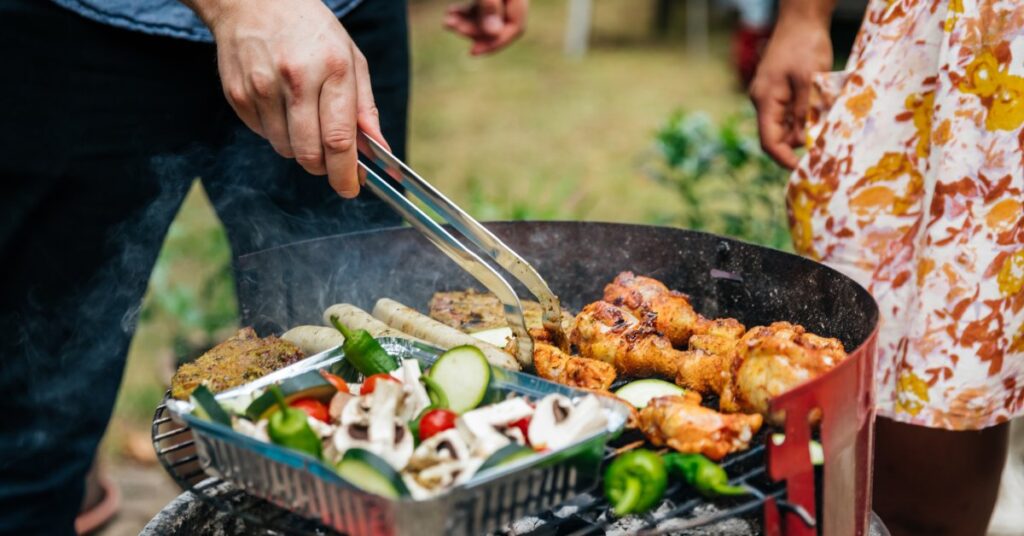
Memorial Day weekend is approaching, and the beginning of summer is in sight. Now that the weather is getting hotter and people are eating and grilling outside again, it's important to make sure your food is safe to eat. The U.S. Department of Agriculture's Food Safety and Inspection Service on Tuesday released four important tips to protect people from foodborne illness.
“Bacteria that cause food poisoning love summer just like the rest of us, because they breed and multiply quickly in warmer temperatures. That's why diseases spike during the summer months,” said Emilio Esteban, Undersecretary for Food Safety. said in a press release. “As we all spend more time outside, it's important to remember these food safety measures to keep your friends and family safe.”
wash hands
We've heard this all the time during the COVID-19 pandemic, and it's still a good rule of thumb. Wet your hands under running water, lather up the soap, rub for 20 seconds, rinse and dry. If running water is not available, use hand sanitizer or a wet towel containing at least 60% alcohol.
Pack fresh food safely
When packing food to prepare and eat outside, store perishables in a cooler or insulated container with a cold source to keep the food at a safe low temperature of 40°F or below. Cold sources include ice, frozen gel packs, and frozen beverages that do not need to be refrigerated to be safe, such as water bottles and iced tea.
It is important to keep the cooler out of the sun. Once outside, place it in the shade to maintain a safe cool temperature. If the cooler is full, perishables can stay half-chilled and safer for longer. Insulated bags also help keep perishables safe when the cooler isn't filled to capacity.
Be aware of how often you open the cooler, as the temperature inside the cooler can fluctuate and create a dangerous environment for fresh food.
Read more: Do you need to wear more sunscreen when it's hot outside?
Keep food away from the “danger zone”.
The “danger zone” is the temperature range between 40°F and 140°F where bacteria grow rapidly. To maintain food safety, fresh produce must be kept out of the “danger zone.”
Cold foods should be kept below 40°F in a refrigerator, cooler, insulated container, or on ice. Hot foods should be placed on the grill, heated chafing dish, slow cooker, or warming tray and kept above 140°F.
Bring an appliance thermometer traditionally used in refrigerators and freezers so you can make sure the food in the cooler remains below the “danger zone.”
Follow the “2 hour rule”
Foods that are not in the “danger zone” or that are not left out for more than two hours can be safely stored. All other foods should be treated as unsafe to eat and should be discarded. Best rule to remember: When in doubt, throw it away.