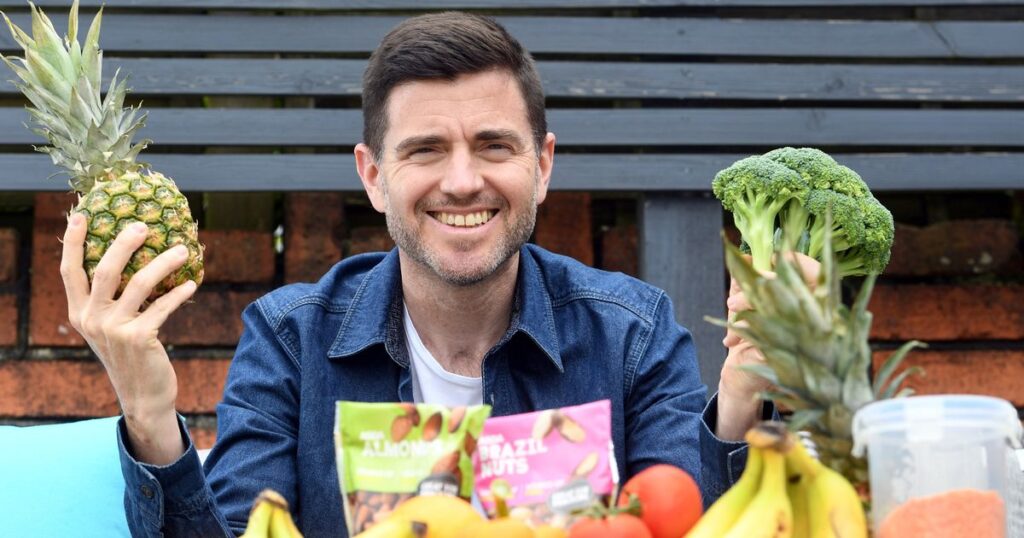
When I decided to cut out refined sugar and ultra-processed food at the start of 2024, I honestly didn’t think I’d last that long.
Like lots of us who start the new year feeling sluggish and unhealthy after eating and drinking too much in December, I thought I’d probably get through January easily, then struggle to go without chocolate or find time to make a breakfast without granola or a quick lunch without bread and crisps.
But six months on, and not only am I managing to stick with it, I’m finding it easy, rewarding and I’m struggling to see how I’d go back to old eating habits. It was initially a bit daunting to think about how I’d remove such “staple” foods from my diet while still being able to eat simple and cheap meals. But it turned out to be simple. In a nutshell, here’s what I did:
no chocolate (or, in fact, any biscuit, dessert or refined sugar)
no ultra-processed foods or ingredients (supermarket bread and granola were the ones I ate most)
less red and processed meat
more legumes (chickpeas, lentils, beans)
more nuts
more olive oil
eating the rainbow (more on this below)
See, we’re not talking anything overly dramatic here. The other key thing I did to learn about what to eat was listen a lot to the Zoe Science and Nutrition podcast. Zoe is a health science company with three co-founders, including Professor Tim Spector, professor of genetic epidemiology at King’s College London and one of the world’s leading researchers (you might have heard his name a lot during Covid, when he was instrumental in the study of symptoms). To be clear at this point: there has been no contact between me and Zoe in relation to this article (or about anything at all, ever) and I am not being paid for this article. I’m just sharing something which I am finding useful and beneficial to my own health.
Read more:I tried Michael Mosley’s Fast 800 diet for a week and couldn’t believe the results
Read more: I was one of 62% of people in Wales overweight – we need to change that
What are ultra-processed foods and which ones do we most commonly eat?
The way we buy food, our busy lives and our squeezed budgets all heavily influence the nature of the food on sale and the food we eat. So do the profit margins of the multi-national corporations that make it. Supermarket shelves are absolutely packed with ultra-processed foods, so much so that it can feel hard to avoid. But it’s actually not that hard at all — and it definitely doesn’t involve eating nothing but fresh fruit and vegetables. Some of the most common ultra-processed foods (or UPFs) are:
supermarket packaged bread
breakfast cereals and granola
flavoured yoghurt
chocolate, biscuits and crisps
energy and granola bars
fizzy drinks
microwave ready meals
For me, the big shocks here were granola and flavoured yoghurt. Before this year, granola was what I ate for breakfast every single day, assuming it was healthy (or at least healthier than cereal). I ate it with fruit and flavoured yoghurt so I thought I was starting the day healthily. In fact, I was having a breakfast massively high in added sugar and ultra-processed ingredients (though you can find ready meals or a certain brand of granola that aren’t ultra-processed).
It’s important to remember that humans have been processing food for thousands of years. Bread, butter, cheese and (healthier) yoghurt are all processed foods. But ultra-processed food is a step further. Prof Spector says: “Plain yoghurt, nothing added, nothing changed, is processed because you are mixing a basic ingredient, milk, with microbes. You are creating something, that is processing. It is when you take it to the next stage… [adding] various starches, emulsifiers, concentrates, artificial sweeteners and flavourings… that same yoghurt becomes ultra-processed. It is that extra step that is the main problem. It is when chemicals that you don’t find in your kitchen are being added to foods that have been stripped of all their goodness… to make it look like food again.”
Dr Chris Van Tulleken, an infectious diseases doctor at University College London, BBC science presenter and New York Times bestselling author, gave this simple one-sentence definition on ultra-processed food on the Zoe podcast: “If it’s wrapped in plastic and it contains at least one ingredient that you don’t typically find in a domestic kitchen, then it’s ultra-processed food.”
(For an experiment, Dr Van Tulleken drastically changed his diet so that 80% of it was made up of ultra-processed food, which would in fact be typical for a teenager in the UK and US. The results were dramatic. He said: “I just ate what I wanted, but with 80% of my calories coming from ultra-processed food. And what happened? I gained a huge amount of weight in one month. I gained so much weight that if I’d continued for the whole year, I would’ve doubled my body weight.”)
What changes did I make and what three foods can I not now live without?
I don’t think I was leading an unusually unhealthy lifestyle before this year. I do a couple of circuits classes a week, run and cycle when I can and already ate a decent amount of fruit and vegetables, while almost always cooking from scratch and never really eating ready meals (I hope this doesn’t make me sound annoying — I’m still a tired 44-year-old with a dad bod if that helps).
But UPFs would get into my diet in other ways. As well as my daily bowl of granola, I’d sometimes grab a supermarket pizza for a quick dinner when pressed for time, or make a sandwich with supermarket bread for lunch, which I’d have with crisps on the side.
So I started to think about how I could still keep my meals tasty while stripping out the unhealthy bits. The three single biggest things I’m doing are:
cooking more legumes either as a main or side part of a meal
eating nuts with Greek yoghurt and fruit for breakfast instead of granola
using more olive oil (though the soaring price is killing me)
eating more vegetables
And the three things I really couldn’t go without now are the legumes, the nuts and the Greek yoghurt.
I’ve started eating far more legumes like cannellini beans
One of the best things about this is cost. It’s common to assume that eating healthier is more expensive. But a tin of beans (cannellini, black, kidney etc) at Asda costs 49p. A cabbage costs 50p and results in a lot of food once you’ve chopped it all up (try frying it with hazelnuts or cashews). A bag of carrots costs 35p. A tin of pineapple chunks costs £1.10 (a real pineapple currently costs 90p – even better!) An avocado costs 95p. You can also use frozen fruit and veg without compromising on the nutrient value and quality of their fresh equivalent. It’s cheaper and lasts longer.
Plants are also high in protein and fibre so they fill you up. I’m not vegan and I’ve not quit meat but I am finding myself eating less, especially red meat, as I find that things like nuts and legumes do a good job of filling you up.
My typical breakfast, lunch and dinner
Breakfast: nuts (usually cashews, almonds or walnuts) with Greek yoghurt and fruit
Lunch: I work mostly in an office in Cardiff city centre so I usually get a salad from the market and go heavy on lentils, veg and hummus. If at home, I might have homemade guacamole or homemade hummus made from chickpeas or butter beans (recipe below), an omelette with onions and peppers, or a baked potato.
Dinner: Fish or chicken with legumes or brown rice, or a bean chilli.
Some of my favourite new recipes
Chicken fajita rice bowl: this has chicken, peppers, red onions, baby corn, lime and black beans. You can make enough to last more than one family meal. You could also add avocado/guacamole on the side. See the recipe here.
Vegan chilli: This is made with lots of different kinds of beans. See the recipe here. You can also stir through some roasted sweet potato to bulk it out more and get more meals from it.
Fish with cannellini beans and courgettes: I make a much-simplified version of this recipe, which doesn’t include the wine, chicken stock, garlic, parmesan or bay leaves. Basically, it’s courgette, lemon, onion and the beans, then fry or roast some fish and stick it on top or on the side. Add fresh mint to the beans at the end to make it even nicer.
Chickpea or butter bean hummus: Hummus is so easy. Just chuck a few ingredients in a blender. Example recipe here. I find swapping butter beans in for chickpeas makes it softer.
Homemade pesto: As with hummus above, throw some ingredients in a blender and you’re done in seconds. Recipe here.
Spaghetti bolognese: This is just a tip on a simple change you can make if you really just fancy something traditional and comforting. Just use less minced beef and use lentils or mushrooms instead to bulk it out.
What is most difficult and what could be even better?
There is one really obvious area where more change would be even more beneficial: alcohol. You will hear some people say that you can’t fully achieve health goals while still drinking alcohol. That may be true, but as a stressed dad with a busy job, my Friday night wine and occasional nights out at the pub with friends and a few pints are things I’m not prepared to give up yet. Everyone needs something, right?
It’s also hard (although a lot less hard than I thought, and it gets easier all the time) to resist the chocolate in the cupboard. I absolutely love it. You could put all the Michelin-starred chefs in the world in a kitchen together and they wouldn’t come up with something that tastes nicer than Nutella.
But two simple options to help eat less sugar-and-chemical-packed chocolates and desserts are:
replace your usual chocolate with a high quality dark chocolate. If it is not too processed and still has a high cocoa percentage, it will still be largely plant-based, have a low amount of added sugar and contain the nutrients and fibres of fruit and vegetables — in fact, Prof Spector calls them “rocket fuel for your gut microbes”
make delicious desserts with fruit or just eat it in its basic form (pineapple and bananas are so sweet and delicious and you can caramelise them by frying them).
What about feeding fussy children?
This is hard. Very hard. I have two young children and one, in particular, is a really fussy eater who won’t eat much beyond fish fingers and Kit-Kats, which I find quite stressful. I want my kids to eat well and not fill their diets with sugar and chemicals. Even when I try and feed the whole family with, say, a homemade lasagne, he point blank won’t have it and I have to cook him something else (usually fish fingers and a Kit-Kat). So at the moment, all I can say is that this is an ongoing process and, for now, I’ll just try to gradually change what’s available to eat in the house for snacks so that there are fewer biscuits and chocolate bars and more fruit. Other than that, I’ll just try my best to model the eating behaviour I want to see.
What have I learned so far and what are my key tips?
I can’t give you a sensational headline about losing two stone in a month. I don’t own weighing scales and, even if I did, I didn’t weigh myself when I first changed my diet. But I feel slimmer and clothes fit a bit more comfortably than they did at the end of 2023 (wearing a shirt doesn’t now feel like I’m being strangled while having my love handles jabbed). I find I can handle exercise a bit easier too and that I’m hungry less often. Don’t get me wrong, by midday I’m starving for lunch. And I still have two young kids and a stressful job so my sleep is poor and I still regularly feel pretty tired. I definitely don’t leap out of bed full of energy every day.
I have no expertise in science or nutrition and it’s been too short a period to determine any sort of long-term benefits but the Zoe website says “whatever your age, if you switch from an unhealthy to a healthy eating pattern, you’ll likely see improvements in your cholesterol levels, blood sugar, inflammation, and weight (Prof Spector gives two foods to reduce inflammation and improve joint pain here)”
Here are my main tips:
cut out pre-made sauces and make them from scratch instead (you can make mayo with four ingredients, and the same goes for pesto and hummus, which are delicious and go great with carrots, celery or fresh sourdough bread)
beans are tastier than anyone has ever given them credit for — stock up on tins and cook them with herbs (black beans and fresh coriander and lime are a great side dish)
nuts are great: they’re filling, healthy and taste delicious raw but even nicer cooked (fry them dry in a pan until they’re golden brown and add them to chopped chicken or a fried/sautéed veg dish)
listen to the Zoe podcast — it makes food and nutrition so much easier to understand
eggs go with most things and can be made into so many different meals
eat the rainbow: this just means mixing and matching plant foods with different colours. Food variety is important and different colours mean different compounds and good chemicals which help your health
you don’t need to make meat the centrepiece of a meal. I have not given up meat, in my house I wouldn’t be allowed to anyway, but there has been a gradual shift away from big meaty centrepieces towards a greater variety of filling and satisfying vegetables dishes
fat is fine: nuts, avocado, olive oil, yoghurt are all full of healthy fats. It’s the unhealthy fats and sugar in UPFs and meat that you need to try to limit
if you can’t imagine life without bread, think about ditching the mass-produced white supermarket bread and grab some freshly-made sourdough bread from a local bakery. It will likely have far fewer chemicals in it – but it will cost a hell of a lot more, upwards of £3-4 a loaf. I buy a loaf every two or three weeks as a weekend treat and have it with olive oil instead of butter (not that you should be scared of a bit of butter)
you don’t have to completely cut out anything at all — even moderate improvements will have corresponding benefits.
The overarching, simple message from the science and nutrition experts who contribute to Zoe is to focus on eating more whole foods and plants, while eating fewer foods which contain a lot of ingredients you’ve never heard of and would never have in your kitchen. A recent study cited by Zoe found that switching from an unhealthy to a healthy diet at the age of 40 can add a decade to your life.
You can also delve a lot deeper to understand the impact of polyphenols and the gut microbiome on your health. For me, that gradual switch in diet sounds like a sensible place to start.